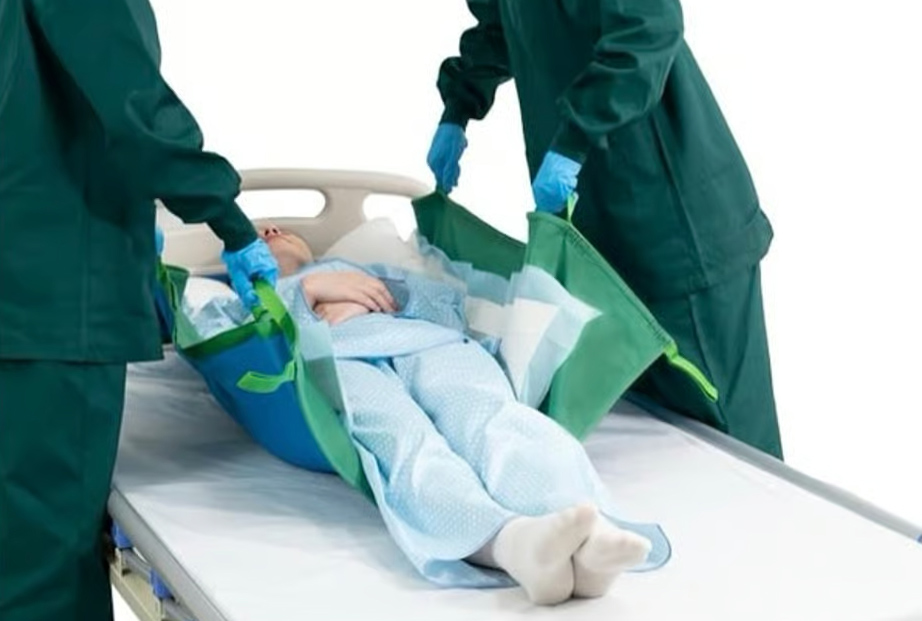
Patient transfers are essential in healthcare, but they also present a significant risk to patient skin integrity. Fragile skin, especially in elderly or compromised patients, can be easily damaged by the forces of shear and friction that occur during manual handling. Fortunately, innovative tools like transfer sheets are specifically designed to mitigate these risks. This post will delve into how the unique anti-shear and friction-reducing properties of transfer sheets play a vital role in protecting patient skin during transfers, contributing to safer and more comfortable care.
1. The Hidden Dangers: Shear and Friction in Patient Transfers
Understanding the forces at play during patient transfers is key to appreciating the value of transfer sheets:
- Friction: This is the resistance that occurs when two surfaces rub against each other. During a manual patient transfer, friction happens between the patient’s skin and the bed surface, or between layers of bedding. This rubbing can strip away the outer layer of skin, leading to abrasions and skin tears.
- Shear: This occurs when layers of skin and underlying tissue are pulled in opposite directions. When a patient is pulled across a surface without their body moving uniformly, the skeleton might move while the skin stays relatively in place, causing internal tissue damage that can lead to pressure ulcers.
Both friction and shear are significant contributors to skin breakdown, pain, and increased risk of infection for patients.
2. How Transfer Sheets Combat Friction: The Smooth Glide
Transfer sheets are typically made from materials with a very low coefficient of friction, such as nylon or specialized synthetic fabrics. This smooth surface is crucial for reducing friction:
- Minimizing Surface Resistance: The slick material of the transfer sheet drastically reduces the resistance between the patient’s body and the bed surface.
- Effortless Gliding: Instead of being dragged, the patient can be smoothly glided across the surface with minimal rubbing against their skin.
- Protecting the Epidermis: By reducing friction, transfer sheets prevent the abrasive forces that can cause superficial skin damage like abrasions and skin tears.
3. How Transfer Sheets Combat Shear: Moving as One
The ability of a transfer sheet to allow the patient’s entire body to move as a single unit is key to combating shear forces:
- Facilitating Uniform Movement: When using a transfer sheet, caregivers can move the patient’s head, torso, and limbs simultaneously and uniformly.
- Preventing Stretching and Distortion: This synchronized movement prevents the stretching and distortion of skin and underlying tissues that cause shear.
- Reducing Internal Tissue Damage: By eliminating shear forces, transfer sheets help protect the deeper tissues, reducing the risk of internal tissue damage that can precede pressure ulcer development.
4. The Benefits of Reducing Skin Damage
Preventing skin damage during patient transfers has wide-ranging positive impacts:
- Improved Patient Comfort: Minimizing skin irritation and injury directly leads to greater patient comfort during and after transfers.
- Reduced Pain: Preventing skin tears and bruising helps to alleviate pain associated with damaged skin.
- Lower Risk of Infection: Damaged skin is more susceptible to infection. Protecting skin integrity reduces this risk.
- Faster Healing: Preventing new skin damage allows existing wounds or incisions to heal more effectively.
- Decreased Healthcare Costs: Treating skin tears, pressure ulcers, and infections is costly. Prevention through the use of transfer sheets can lead to significant cost savings.
- Enhanced Patient Satisfaction: Patients who experience comfortable and injury-free transfers are likely to have a more positive perception of the care they receive.
5. Choosing the Right Transfer Sheet for Skin Protection
When selecting transfer sheets, consider properties that maximize skin protection:
- Material: Look for low-friction, durable, and breathable synthetic materials.
- Construction: Ensure the sheet is well-constructed with smooth seams to avoid creating pressure points.
- Size and Weight Capacity: Choose a sheet appropriate for the patient’s size and weight to ensure proper function.
6. Proper Usage Remains Crucial
While transfer sheets are powerful tools, their effectiveness in preventing skin damage is amplified by proper usage techniques. Caregivers should be trained on the correct methods for positioning the sheet, gripping it securely, and moving the patient smoothly and uniformly to fully leverage the anti-shear and friction-reducing properties.
7. Conclusion: Transfer Sheets – Essential for Protecting Patient Skin
Patient skin integrity is a critical component of quality care. The forces of shear and friction during transfers pose a real threat to this integrity. Transfer sheets, with their inherent anti-shear and friction-reducing properties, offer a simple yet vital solution. By facilitating smooth, effortless transfers that allow the patient’s body to move as a unit, transfer sheets significantly reduce the risk of skin tears, bruising, and contribute to preventing pressure ulcers. Implementing and consistently using high-quality transfer sheets is an essential step towards creating a safer, more comfortable, and more compassionate environment for vulnerable patients during the necessary process of transfer.